Collection集合常用功能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public static void main(String[] args){ Collection<String> coll=new ArrayList<>(); //向集合中添加元素 coll.add("hello" ); coll.add("zhong" ); coll.add("guo" ); System.out.println(coll); //删除集合中的某个元素 boolean r=coll.remove("hello" ); System.out.println(coll); //清空集合 coll.clear(); System.out.println(coll); //判断集合中是否包含某个元素 boolean f=coll.contains("guo" ); System.out.println(f); //判断集合是否为空 System.out.println(coll.isEmpty()); //获取集合的长度 System.out.println(coll.size()); //将集合转成一个数组 Object[] arr = coll.toArray(); for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) System.out.println(arr[i]); } 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829
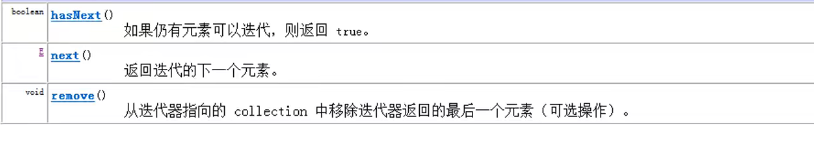
Iterator迭代器 Iterator接口也是Java集合中的一员,但它与Collection、Map接口有所不同
Collection接口 与Map接口主要用于存储元素,而Iterator主要用于 迭代访问(即遍历) Collection中的元素,因此Iterator对象也被称为迭代器
那么迭代是什么意思?
即Collection集合元素的通用获取方式。在取元素之前先要判断集合中有没有元素,如果有,就把这个元素取出来,继续在判断,如果还有就再取出来,一直把集合中的所有元素全部取出
Iterator接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public static void main(String[] args){ Collection<String> coll= new ArrayList<>(); coll.add("AAA" ); coll.add("BBB" ); coll.add("CCC" ); coll.add("DDD" ); coll.add("EEE" ); coll.add("FFF" ); Iterator<String> it=coll.iterator(); //判断还有没有下一个元素,有则返回true //boolean b=it.hasNext(); //System.out.println(b);//true //String s =it.next(); //System.out.println(s);//AAA //boolean b1=it.hasNext(); //System.out.println(b1);//true //String s1 =it.next(); //System.out.println(s1);//BBB //上面的输出方法太麻烦了, //循环结束的条件是:hasNext方法返回false //迭代方法遍历 while (it.hasNext()) { String e=it.next(); System.out.println(e); } //for循环遍历 for (Iterator<String> it2=coll.iterator();it2.hasNext();){ String e=it2.next(); System.out.println(e); } } 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041
LinkedList集合
Set集合存储元素不重复的原理
HashSet存储自定义类型元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 //实现同名同年龄的人只能存储一次 //必须重写hashCode方法和equals方法 public static void main(String[] args){ //创建HashSet集合存储person HashSet<person> s=new HashSet<>(); person p=new person("张三" ,18); person p1=new person("张三" ,18); person p2=new person("王五" ,22); System.out.println(p.hashCode());//764977973 System.out.println(p1.hashCode());//381259350 System.out.println(p1==p);//false 哈希值不同 System.out.println(p.equals(p1));//false s.add(p); s.add(p1); s.add(p2); System.out.println(s); } 123456789101112131415161718192021 public class person extends Object{ private String name; private int age; public person } public person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } //添加下面这段代码,重写hashCode方法和equals方法 @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; person person = (person) o; return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name); } @Override public int hashCode return Objects.hash (name, age); } @Override public String toString return "person{" + "name='" + name + '\' ' + ", age=" + age + ' }'; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } 123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051
LinkedHashSet集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 /* LinkedHashSet集合extends HashSet集合 LinkedHashSet集合特点: 底层是一个哈希表(数组+链表/红黑树)+链表:多了一条链表(记录元素的存储顺序),保证元素有序 */ public static void main(String[] args){ //创建HashSet集合存储person HashSet<String> s=new HashSet<>(); s.add("abc" ); s.add("abc" ); s.add("hello" ); s.add("world" ); System.out.println(s);//[abc, world, hello] 无序 不允许重复 LinkedHashSet<String> s1=new LinkedHashSet<>(); s1.add("abc" ); s1.add("abc" ); s1.add("hello" ); s1.add("world" ); System.out.println(s1);//[abc, hello, world]有序 不允许重复 1234567891011121314151617181920212223
可变参数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 /* 可变参数 使用前提 当方法的参数列表数据类型已经确定,但是参数的个数不确定,就可以使用可变参数 使用格式 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(数据类型...变量名){} 可变参数的原理: 底层是一个数组,根据传递参数个数不同,创建不同长度的数组,传递的参数可以是任意个 注意 一个方法的参数列表只能有一个可变参数 如果方法的参数有多个,那么可变参数必须写在参数列表的末尾 */ public static void main(String[] args) { int i=add(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10); System.out.println(i); } public static int add(int...arr){ int ans=0; for (int i:arr) { ans+=i; } return ans; } //可变参数的终极写法,可以传入任意类型的参数 public static void method(Object...obj){ } 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829
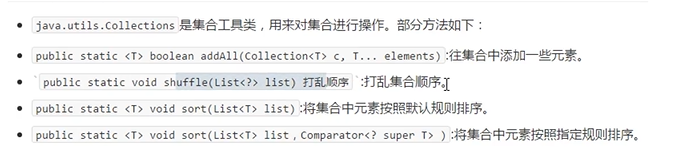
Collections集合常用功能 注意这个是Collections(+s的哦),和前面的是不一样的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 /* Comparator和Comparable的区别 Comparable:自己(this)和别人(参数)比较,自己需要实现Comparable接口,重写比较的规则compareTo方法 Comparator:相当于找一个第三方裁判,比较两个 */ public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); /* list.add("a" ); list.add("b" ); list.add("c" ); System.out.println(list);//[a, b, c] */ //如果需要存大量数据 Collections.addAll(list,"a" ,"b" ,"c" ); System.out.println(list);//[a, b, c] //打乱集合顺序Integer Collections.shuffle(list); System.out.println(list);//[c, b, a] ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(list1,1,5,6,2,4,7,8,9); //默认是从小到大 Collections.sort (list1); System.out.println(list1);//[1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] // ArrayList<person> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); list2.add(new person("张三" ,21)); list2.add(new person("李四" ,20)); list2.add(new person("王五" ,19)); System.out.println(list2); //sort使用前提 //该排序的集合里面存储的元素,必须实现Comparable,重写接口中的方法compareTo定义排序的规则 //Comparable排序 //return this.getAge()-o.getAge();//年龄从小到大 //return o.getAge()-this.getAge();//年龄从大到小 Collections.sort (list2); System.out.println(list2); ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>(); list3.add(3); list3.add(4); list3.add(1); list3.add(2); System.out.println(list3); Collections.sort (list3, new Comparator<Integer>() { //重写比较的规则 @Override public int compare(Integer t1, Integer t2) { // return 0; // return t1-t2;//升序 return t2-t1;//降序 } }); System.out.println(list3); } 123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657 public class person implements Comparable<person>{ private String name; private int age; public person } @Override public String toString return "person{" + "name='" + name + '\' ' + ", age=" + age + ' }'; } public person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } //重写排序的规则 @Override public int compareTo(person o) { //return 0; //return this.getAge()-o.getAge();//年龄从小到大 return o.getAge()-this.getAge();//年龄从大到小 } } 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344
Map集合 Map<K,V> ,k-此映射所维护的键的类型 ,v-映射值的类型
一个映射不能包含重复的键,每个键最多只能映射到一个值
Map集合的特点:
HashMap特点:
HashMap底层是哈希表,查询速度快
LinkedMap特点:
1.LinkedHashMap 集合底层是哈希表+链表
2.LinkedHashMap集合是一个有序的结合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序一致
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 public static void main(String[] args) { demo01();//put:把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中 demo02();//remove:把指定的键所对应的键值对元素在map集合中删除 demo03();//containsKey:判断结合中是否包含指定的键 demo04();//get:根据指定的键,在map集合中获取对应的值 } public static void demo01 //put操作 Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>(); //存储键值对的时候,key不重复,返回值v是null //存储键值对的时候,key重复,会使用新的value替换map中重复的value,返回被替换的value值 String str = map.put("张三" , "李四" ); System.out.println(str);//null String str1 = map.put("张三" , "李四123" ); System.out.println(str1);//李四 System.out.println(map);//{张三=李四123} map.put("王五" ,"赵六" ); map.put("a" ,"c" ); map.put("b" ,"c" ); System.out.println(map);//{a=c, 张三=李四123, b=c, 王五=赵六} } public static void demo02 //remove操作 //key存在,v返回被删除的值 //key不存在,v返回null; Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("x" ,1); map.put("y" ,2); map.put("z" ,3); Integer x1 = map.remove("x" ); System.out.println(x1);//1 Integer x2 = map.remove("a" ); System.out.println(x2);//null System.out.println(map);//{y=2, z=3} } public static void demo03 //containsKey操作 //key存在,返回true //key不存在,返回false ; Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("x" ,1); map.put("y" ,2); map.put("z" ,3); boolean y1=map.containsKey("x" ); System.out.println(y1);//true boolean y2=map.containsKey("a" ); System.out.println(y2);//false } public static void demo04 //get操作 //key存在,返回v //key不存在,返回null; Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("x" ,1); map.put("y" ,2); map.put("z" ,3); Integer z1=map.get("x" ); System.out.println(z1);//1 Integer z2=map.get("a" ); System.out.println(z2);//null } 123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778
Map集合的遍历方式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 //keyset用法 public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("x" ,1); map.put("y" ,2); map.put("z" ,3); Set<String> set = map.keySet(); //使用迭代器 Iterator<String> it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ String key=it.next(); Integer value=map.get(key); System.out.println(key+"=" +value); } //使用增强for for (String key:set ){ Integer value=map.get(key); System.out.println(key+"=" +value); } //增强for 简化版 for (String key:map.keySet()){ Integer value=map.get(key); System.out.println(key+"=" +value); } } 123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627 //EntrySet用法 /* Map集合的第二种遍历方式:使用Entry对象遍历 Map集合中的方法: set <Map.Entry<K,V>> entryset() 返回此映射中包含的键的set 视图 实现步骤: 1.使用Map集合的方法entryset(),把Map集合多个yEntr取出来,存储到一个set 集合中 2.遍历set 集合,获取每一个Entry对象 3.使用Entry对象中的方法getkey()和getValue()获取键与值 */ public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("x" ,1); map.put("y" ,2); map.put("z" ,3); Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet(); // Set<String> set = map.keySet(); //使用迭代器 Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ Map.Entry<String, Integer> nx = it.next(); String key = nx.getKey(); Integer value = nx.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"=" +value); } //使用增强for for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:set ){ String key = entry.getKey(); Integer value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"=" +value); } } 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435
Hashtable集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 /* Hashtable :底层是哈希表,不能存储null值,null键 */ public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<String,String> mp=new HashMap<>(); mp.put(null,"a" );// 这种情况存储不进去但不会报错 mp.put("b" ,null); mp.put(null,null); System.out.println(mp); Hashtable<String,String> table=new Hashtable<>(); table.put("1" ,"a" ); table.put("b" ,"2" ); // table.put(null,null);//这种情况会报错 System.out.println(table); } 12345678910111213141516
JDK9对集合添加元素的优化—of方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 /* list接口、Set接口、Map接口,里面增加了一个静态的方法of,可以给集合一次性添加多个元素 使用前提: 当集合中存储的元素的个数已经确定了,不在改变时使用 注意: of方法只适用于list接口、set 接口、Map接口,不适用于接接口的实现类 of方法的返回值是一个不能改变的集合,集合不能在使用add,put方法添加元素,会抛出异常 set 接口和Map接口在调用of方法的时候,不能有重复的元素,否则会抛出异常 */ public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> a = List.of("a" , "b" , "c" ); System.out.println(a); //Set<String> b = Set.of("1" ,"1" ,"2" , "3" );//错误,不可重复 Set<String> b = Set.of("1" ,"2" , "3" ); System.out.println(b); //Map<String, String> x = Map.of("x" , "1" , "y" , "2" ,"x" ,"3" );//x重复 Map<String, String> x = Map.of("x" , "1" , "y" , "2" ); System.out.println(x); }